

As for Mother Clap, she was present all the Time, except when she went out to fetch Liquors… The Company talk’d all manner of gross and vile Obscenity in her hearing, and she appeared to be wonderfully pleas’d with it.
The trial of Margaret Clap, April 1726,
Select Trials for Murders, Robberies, Rapes, Sodomy… (Published in 1742)
Margaret Clap was a bold ally for a persecuted community in London during the 1720s. She welcomed gay men to drink and sleep at her husband’s house in Holborn, earning her the nickname ‘Mother Clap’. Clap defended her customers against the Buggery Act’s outlawing of gay sexual activity as a sin punishable by death—lying on their behalf to have them acquitted of such charges. Her allyship was suppressed, however, when her venue was infiltrated by a constable from the Societies for the Reformation of Manners, pretending to be the husband of one of Clap’s customers. Members of these fervently religious Societies subsequently raided her house and had her arrested for encouraging buggery.
Mother Clap and those she supported were early victims of the kind of religiously motivated ‘moral’ campaigns which would be used to justify the suppression of materials deemed to be blasphemous in the early 19th century, centuries of opposition to reproductive rights, and the prosecution by Mary Whitehouse of Gay News, which influenced the formation of LGBT Humanists in 1979.
The surviving records of Clap’s life are mainly found in transcripts of trials induced by the Societies for the Reformation of Manners against Clap and her customers. They provide a glimpse into the fascinating phenomena of molly houses—venues primarily for gay men who met for companionship, sex, and freedom of expression such as cross-dressing.
For example, Clap is documented to have rented accommodation to same-sex couples and facilitated ceremonies in her Marrying Room. These irreverent events enabled a tailored and unique approach to ceremony, suited to the participants themselves— elements later found in secular Owenite namings, and throughout the long tradition of humanist ceremonies.
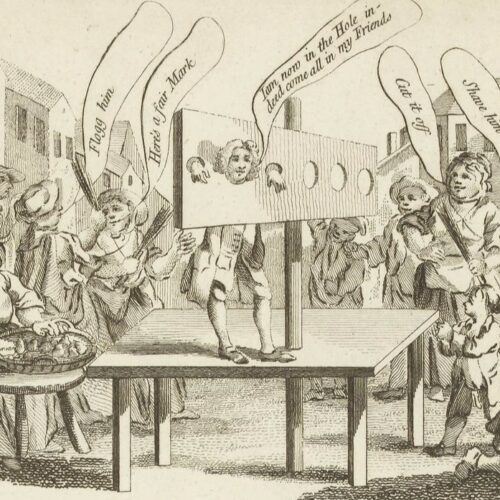
Although Clap was prosecuted for keeping a ‘disorderly house’, hers was not a brothel. It served a key social function, with Clap’s income deriving from rented rooms and the provision of drink. Clap was ultimately ordered to stand in the pillory in Smithfield Market, fined 20 marks, and sentenced to two years’ imprisonment. Treated with public disdain on the pillory, it is believed that she did not survive prison.
Through her kindness, legal advocacy, and the provision of safe spaces for free expression, Clap championed humanist principles of compassion, acceptance, and the right to self expression. Willing to challenge social norms and the law itself, she demonstrated a commitment to activism for those persecuted on religious grounds to be treated instead with respect and dignity.
Mother Clap is one of the historical figures featured in Picturing Nonconformity: LGBT Humanist Heritage, created for the 45th anniversary of LGBT Humanists in 2024. Explore the exhibition.
Reformation of Manners Campaigns | London Lives
Mother Clap’s Molly House | City of London
The raid on Mother Clap’s Molly House | The Historians Magazine
Clap, Margaret [known as Mother Clap] by Rictor Norton | Oxford Dictionary of National Biography
Main image: From ‘This is not the thing: or, Molly exalted‘, 1762. © The Trustees of the British Museum, CC BY-NC-SA 4.0

Why are these minds left without the means of obtaining that knowledge which they so ardently desire and why are […]

The Humanist Housing Association began in January 1955, founded as the Ethical Union Housing Association to provide affordable homes for […]

If the basic cause of an unsuccessful marriage is removable, conciliation is the proper procedure. If it is not removable, […]

Its main concern is with peace and security and with human welfare, in so far as they can be subserved […]